Label(标签)是 Kubernetes 资源管理的基础机制之一,通过灵活的标签体系,可以高效地组织、筛选和管理集群中的各类对象,是实现自动化运维和资源治理的关键。
Label 是附着到 Kubernetes 对象(如 Pod、Service 等)上的键值对标签。可以在对象创建时指定,也可后续添加或修改。Label 的值对系统本身没有语义,仅用于用户识别和资源组织。
下面是一个典型的 Label 配置示例:
"labels": {
"app": "nginx",
"version": "v1.2.0",
"environment": "production"
}
Kubernetes 会为 Label 建立索引和反向索引,以优化查询和监听操作。在 UI 和命令行中,Label 会按字母顺序排序显示。建议不要在 Label 中存储大型或结构化数据,这类信息应使用 Annotation。
合理设计 Label 能将组织架构映射到系统架构,便于微服务管理和运维。常见标签类型包括环境、架构、业务、版本等。
environment: dev|staging|production,release: stable|canary|betatier: frontend|backend|database,component: web|api|cacheteam: platform|product|data,project: project-a|project-b,customer: customer-x|customer-yversion: v1.2.0,track: daily|weekly通过统一的标签规范,可以实现资源的灵活分组与高效检索。
Label 的 key 和 value 均有严格的格式要求,确保标签的唯一性和可读性。
prefix/name,用 / 分隔kubernetes.io/ 和 k8s.io/ 前缀为 Kubernetes 保留-)、下划线(_)、点(.)-)、下划线(_)、点(.)Label Selector 用于根据标签筛选对象集合,是 Kubernetes 资源编排的核心能力。主要分为等值选择器和集合选择器两种。
等值选择器通过 =、==、!= 操作符筛选对象。如下示例:
以下命令选择环境为 production 且层级为 frontend 的 Pod:
kubectl get pods -l environment=production,tier=frontend
选择不在 development 环境的 Pod:
kubectl get pods -l environment!=development
集合选择器通过 in、notin、exists 操作符实现更复杂的筛选逻辑。
选择环境为 production 或 qa 的 Pod:
kubectl get pods -l 'environment in (production,qa)'
选择层级为 frontend 但环境不是 development 的 Pod:
kubectl get pods -l 'tier in (frontend),environment notin (development)'
选择包含 environment 标签的 Pod(无论值是什么):
kubectl get pods -l environment
选择不包含 environment 标签的 Pod:
kubectl get pods -l '!environment'
下图展示了 Label Selector 如何通过不同的选择器筛选出目标对象:
```mermaid “Label Selector 选择关系” graph TD A[所有 Pod] –> B{environment=production} B –> C{tier=frontend} C –> D[目标 Pod 集合] A –> E{environment!=development} E –> F[非开发环境 Pod]

{width=1920 height=2837}
## Label 在 API 对象中的用法
Label Selector 可在多种 Kubernetes API 对象中使用,支持不同复杂度的选择器。
### 简单选择器
在 Service、ReplicationController 等对象中,常用等值选择器:
以下 YAML 示例展示了 Service 通过 selector 选择目标 Pod:
```yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-service
spec:
selector:
app: nginx
environment: production
ports:
- port: 80
在 Deployment、ReplicaSet、DaemonSet、Job 等对象中,支持复杂的 matchLabels 和 matchExpressions:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
matchExpressions:
- key: tier
operator: In
values: [frontend, backend]
- key: environment
operator: NotIn
values: [development]
- key: version
operator: Exists
在调度策略中,Label Selector 可用于节点亲和性(NodeAffinity)和 Pod 亲和性(PodAffinity)等场景,实现更灵活的调度约束。
以下 YAML 展示了复杂的亲和性配置:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/arch
operator: In
values: [amd64, arm64]
- key: node-type
operator: NotIn
values: [spot]
podAffinity:
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- weight: 100
podAffinityTerm:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
app: cache
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
下图展示了 Service、Pod、Deployment 等对象之间通过 Label 进行关联和选择的关系:
mermaid "Kubernetes 资源与 Label 关联"
graph LR
S(Service) -- selector --> P(Pod)
D(Deployment) -- selector --> P
RS(ReplicaSet) -- selector --> P
P -- labels --> L[Labels]
{width=1920 height=1092}
通过 Label Selector,Service 可以将具有相同标签的 Pod 组合成一个服务对外提供访问。
下图展示了 Label 在服务发现中的作用:
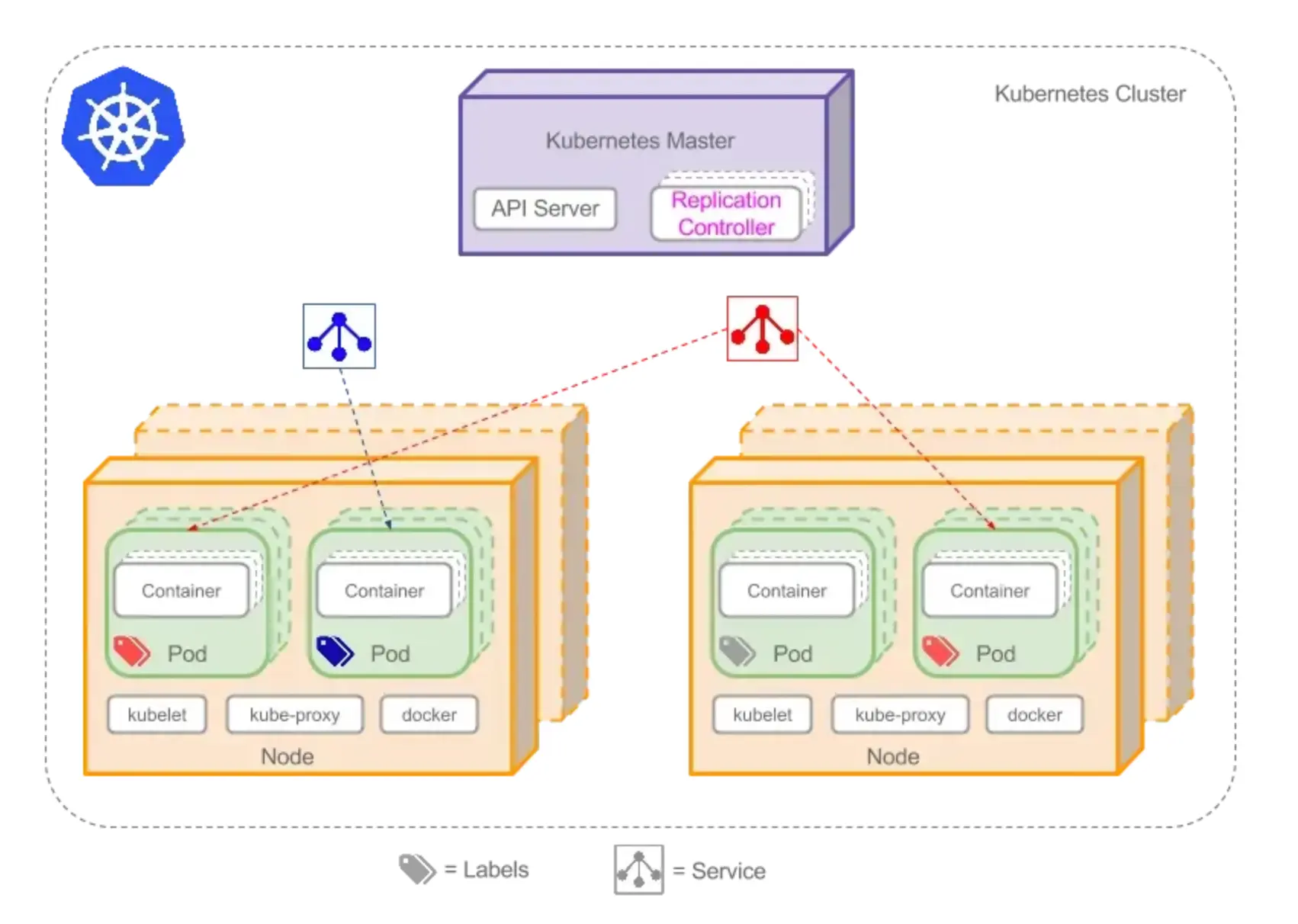 {width=803 height=588}
{width=803 height=588}
在实际使用 Label 时,需注意以下几点:
app、version、environment。Label 是 Kubernetes 资源管理和自动化运维的基石。通过合理设计标签体系和选择器,可以实现资源的灵活分组、精准调度和高效治理。建议在实际项目中制定统一的标签规范,充分发挥 Label 的强大能力。